Sentry Page Protection
SAS Functions [2-14]
SUM Functions
The SUM function allows you to add up values despite the present of missing values.
In SAS, there are two ways to add up numeric values:
- Plus Sign (+) or
- SUM function
The usage of the Plus Sign (+) has been demonstrated in the previous session.
The downside of using the Plus Sign (+) is that the summation will not be performed with the present of missing values.
Let's illustrate this with an example.
Let's illustrate this with an example.
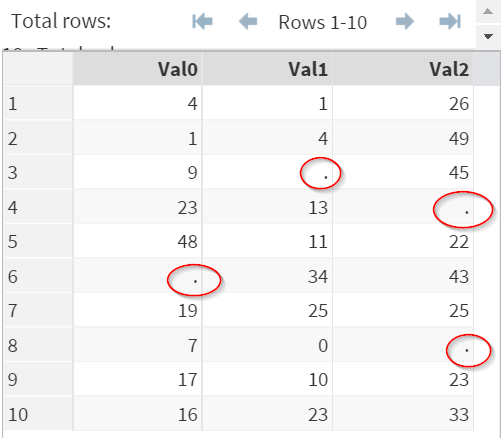
The NUMBERS data set above contains 3 variables: Val0, Val1 and Val2.
[Note: To see the NUMBERS data set on SAS Studio, run the code in the yellow box above]
Some values from the data set are clearly missing.
Now, we're going to add up all 3 variables using the Plus Sign (+).
Example
Data Math1;
Set Numbers;
val3 = val0+val1+val2;
Run;
The numbers were not added up when there are missing values!
This is not good, as you could potentially lose tons of data because of the present of just 1 missing value!
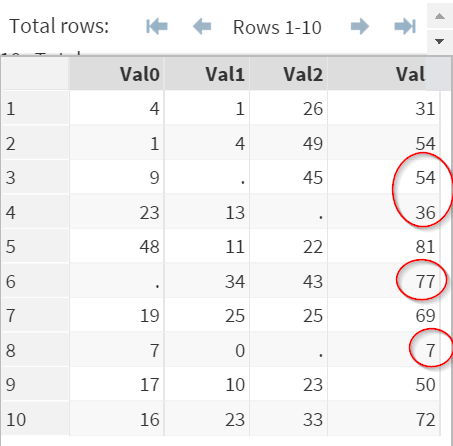
The better way to add up values is to use the SUM function.
Example
Data Math2;
Set Numbers;
Val3 = Sum(of val0, val1, val2);
Run;
The SUM function will ignore any missing values when adding up the numbers.
No data will be lost due to missing values.
Function Structure
The SUM function is structured as:
Sum(of val1, val2, ...);
You can have as many parameters in the SUM function as you want.
Exercise
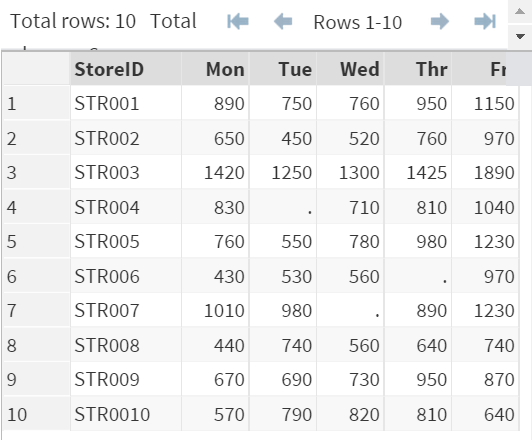
Copy and run the SALES data set from the yellow box below.
Copy and run the SALES data set from the yellow box below.
SALES contains 6 variables:
- STOREID
- MON: SALES (Monday)
- TUE: SALES (Tuesday)
- WED: SALES (Wednesday)
- THR: SALES (Thursday)
- FRI: SALES (Friday)
Write a SAS program to calculate the total sales of the week. Create any data set or variables if necessary.
Need some help?
HINT:
The plus sign (+) will not work when there is missing value.
SOLUTION:
Data Sales_Week;
Set Sales;
Total = Sum(of Mon, Tue, Wed, Thr, Fri);
Run;
Fill out my online form.