Sentry Page Protection
Variable Attributes [17-17]
Attribute #6: Informat
Variable Informat identifies the form of data in SAS.
It is mostly used when (1) reading in an external file, or (2) converting a character variable into a numeric variable.
In this session, we will focus on the latter.
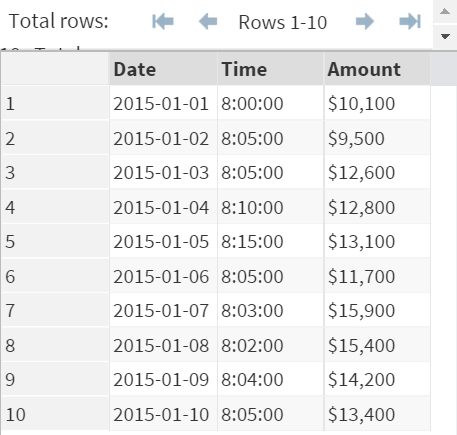
In the CHAR data set, there are 3 variables:
- Date
- Time
- Amount
All 3 variables are character variables.
Having the date, time and amount data in character variables is not recommended, as no calculation can be done on the "text".
INPUT function
As opposed to the PUT function, the INPUT function converts the variable from character back to numeric.
Let's take a look at the following example.
Example
Data Char2;
Set Char;
Date2 = Input(Date, yymmdd10.);
Run;
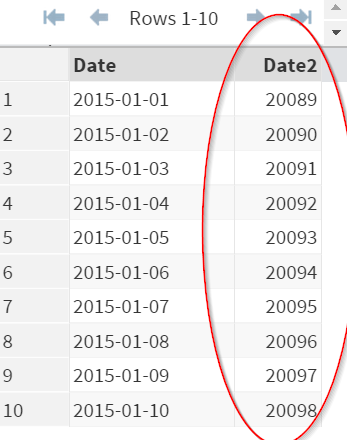
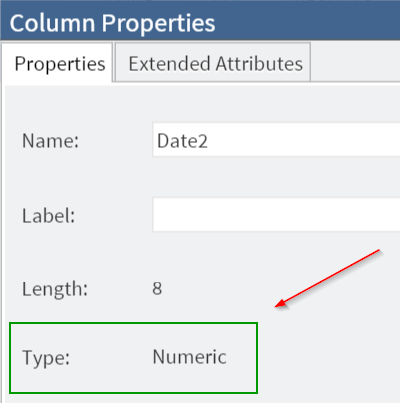
The INPUT function creates a new variable called Date2, which contains the numeric form of the date from the original Date variable.
E.g. 2015-01-01 --> 20089
Date2 is a numeric variable:
Structure of INPUT function
Similar to the PUT function, the INPUT function takes on two parameters:
- The character variable to be converted.
- The informat to use for conversion
In this example, the informat used is (YYMMDD10.).
Selecting the Informat
When using the Input function, you must select an informat that matches the form of the original data.
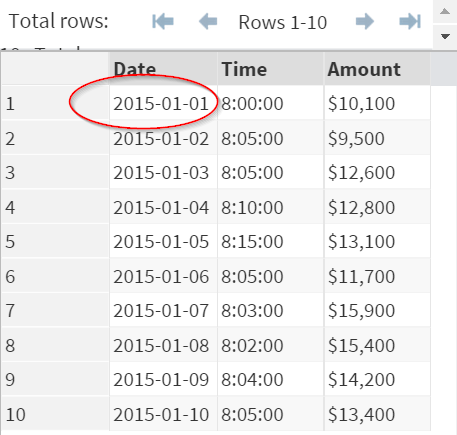
In our example, the data from the Date variable has the form of YYYY-MM-DD:
E.g. 2015-01-01
This matches the informat of (YYMMDD10.).
As a result, the (YYMMDD10.) is used in the Input function.
Let's take a look at another example.
Example
Data Char3;
Set Char;
Time2 = Input(Time, Time8.);
Run;
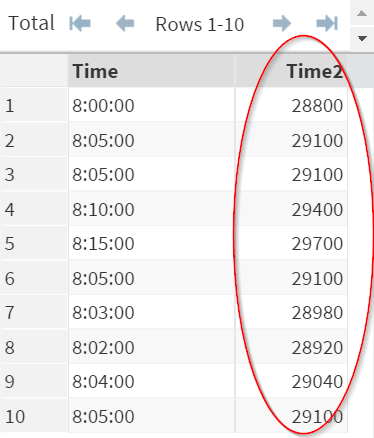
In this example, the data from the Time variable has the form of (HH:MM:SS).
E.g. 8:00:00
This is matched by the informat of (time8.).
Using the informat of (time8.) successfully converts the Time variable from character back to its numeric time representation:
E.g. 8:00:00 --> 28800
Exercise
The Amount variable from the CHAR data set above has yet to be converted into numeric.
Convert the variable into numeric using the Input function.
Convert the variable into numeric using the Input function.
Need some help?
HINT:
The proper Informat for this is (dollar8.).
SOLUTION:
Data Char4;
Set Char;
Amt = Input(Amount, Dollar8.);
Run;
Fill out my online form.