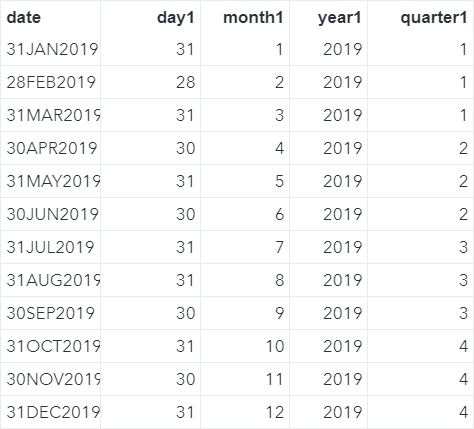|
Sentry Page Protection
Handling Date Values [4-7]
SAS Date Functions In the next few sections, we will look at a number of SAS date functions that allow you to manipulate date values efficiently in SAS.
Example
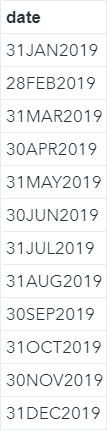
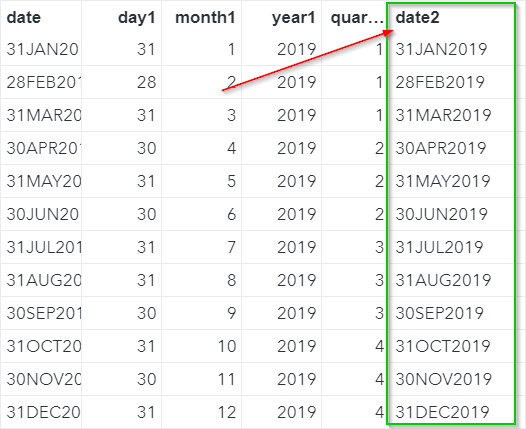
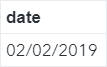
DAY, MONTH, YEAR Functions The DAY, MONTH, YEAR and QTR functions allow you to extract the days, months, years and quarters from given date values. Let's look at some examples. Copy and run the code from the yellow box below: The DATELIST data set contains the last day of the month for each month in 2019. Now, we will extract the days, months, years and quarters from the dates using the corresponding functions. Example data datelist2; set datelist; day1 = day(date); month1 = month(date); year1 = year(date); quarter1 = qtr(date); run; The days, months, years and quarters of the dates are extracted: MDY Function The MDY function does the opposite of the DAY, MONTH and YEAR functions. It combines the day, month and year values into a date variable. Example data datelist2; set datelist; day1 = day(date); month1 = month(date); year1 = year(date); quarter1 = qtr(date); format date2 date9.; date2 = mdy(month1, day1, year1); run; The MDY function combines the MONTH1, DAY1 and YEAR1 variables that we created earlier and creates a new variable called DATE2. TODAY Function The TODAY function returns the current date in SAS. Let's look at an easy example. data testdate; format date mmddyy10.; date = today(); run; The DATE variable is assigned the value from the TODAY function, which returns the current date when the code is run. Exercise
Copy and run the code from the yellow box below: The COUPON data set contains a list of coupons and their expiration day, month and year. Create a new data set called CURRENT_COUPON that contains the coupon code that has not expired as of today's date. Need some help?
HINT: SOLUTION: data current_coupon;
Fill out my online form.
|